Until recently I was under the assumption that I was getting the best milk for my family by getting organic milk from the grocery store. One fine day we visited a local dairy to see how dairy products are made and how it gets from the farm to our fridge.
If you moved from another country you would understand what I am saying. Ever wondered why milk back home made all that cream when heated? Why does the shelf life of milk be a couple of days back home and months here in the United States?

What is non homogenised milk?
Non-homogenized milk is basically milk in its natural state. The key difference is that it hasn’t gone through a process called homogenisation.
Homogenisation process
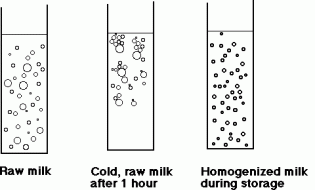
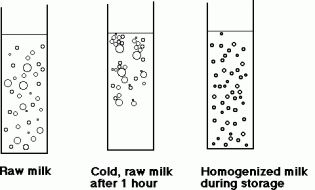
A process called Homogenisation was introduced in the US in 1932. It breaks apart fat molecules under high pressure, leaving the fat suspended and evenly dispersed throughout the milk. As a result of homogenization the cream/fat portion of milk, which normally floats on top, is emulsified with the non-fat portion.
Any guesses why this process became the industry standard? Yes, to market milk to longer distances and increase the shelf life.
What are the benefits of non-homogenised milk?
Non-homogenized milk, also known as cream-top milk, is milk that has not gone through the process of homogenization, where fat droplets are broken down and distributed evenly throughout the liquid. Consuming non-homogenized milk offers several benefits:
1) Natural State and Taste: Non-homogenised milk holds its natural creaminess and texture, providing a richer and more authentic taste. Many people prefer its flavor over homogenized milk.
2) Nutrient Integrity: The natural structure of milk fat globules is preserved in non-homogenised milk, which may help maintain the integrity of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
3) Easier Digestion: Few studies suggest that non-homogenised milk is easier to digest for some people because the fat globules remain in their natural state,aiding in the digestion of other milk components.
4) Potential Health Benefits: There is some evidence that non-homogenised milk has health benefits such as reducing the risk of heart disease. This could be due to the presence of beneficial fats like conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which might be more available in non-homogenized milk.
5) Minimal Processing: Non-homogenised milk is closer to its natural form with minimal processing. Some consumers prefer this as it aligns with a more natural and less industrialized food choice.
6) Support for Local and Small-Scale Farmers: Non-homogenised milk is often produced by small-scale, local farms that prioritize traditional farming methods. Purchasing this type of milk can support these farmers and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
7) Culinary Uses: The cream layer that forms on top of non-homogenised milk can be used in various recipes, adding versatility in the kitchen. This cream can be skimmed off and used separately, making it ideal for making butter, cream-based sauces, or simply adding a rich touch to dishes.
Why you should not be consuming Homogenised milk?
Homogenized milk makes the fat in the milk nearly indigestible. This could likely contribute to heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic disorders, as well as allergies, largely by boosting the absorbability of an enzyme in milk called Xanthine Oxidase XO instead of being excreted. The higher blood levels of XO could contribute to disease-promoting inflammatory processes in our bodies.
If you want to understand and learn more about it physiologically, check this link:
http://www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/milk-homogenization-heart-disease/
Where can you find Non-homogenised milk? What should you be looking for in your milk?
Most of the milk in the United States is homogenised, so you will have to read the label closely
which says Non-homogenized like this one. We are so accustomed to homogenized milk that we have forgotten that it is not in its Natural state. Look at the label. The natural state of milk is like oil in water emulsion. If left to sit over time, you will find its fat portion rising to the top of its water portion and forming a cream layer. Non-homogenized milk does not carry bacteria, as it is still pasteurized. Non-homogenized milk doesn’t carry extra fat either. It just doesn’t mess with the fat.
Whether these studies are true or not, I just feel more comfortable ingesting fat in a more natural state, the way it first existed.
Do you avoid all processed food? But Do you consume Cow’s Milk?
Today’s cow’s milk is free from bad pathogens and safe to consume but all the processes chemically alter the milk making it a highly processed food?
Homogenization is one of the processes contributing to the making of dairy products a far cry from what was used by our ancestors.
Yes, non-homogenised milk is safe to consume as long as it has been pasteurized.
Pasteurisation and homogenisation are two completely different processes when it comes to processing of milk. Pasteurisation kills bacteria and homogenisation breaks down the fat globules. Its important to note non homogenised milk can still be pasteurised.
The milk needs be boiled if it is raw or unpasteurised milk. Bringing raw milk to boil will significantly remove the bacteria making it safer to consume.